BrainVoyager QX v2.8
Probabilistic Maps from Surface Patches-Of-Interest
Probabilistic maps can be calculated from POIs of homologue areas defined on meshes of a group of subjects who participated in cortex-based alignment. The POIs must be defined on the “SPH” versions of subject's cortex meshes. Furthermore, for each subject a respective SSM file (one for the left and one for the right hemisphere) must be available in order to allow transforming the POIs in subject space into the common space achieved during cortex-based alignment. The POIs in aligned space can then be used to calculate a probabilistic map testing the consistency of one or more regions across the cortices of the participating subjects.
While POIs could be trnasformed for individual subjects, it is recommended to integrate the POIs of different subjects into a common POI file as shown below. In this example, two POIs, "PPA_LH" and "FFA_LH" have been defined on the SPH mesh of the left hemisphere of each subject. Using the Load and Add buttons, the data in POI files from single subjects can be integrated in a common group POI file.
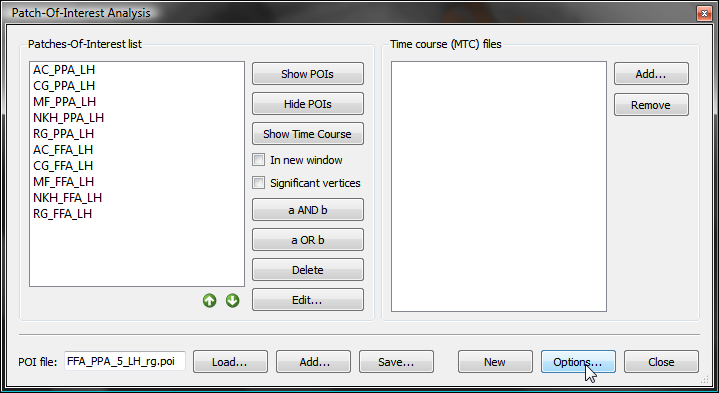
The POI names must uniquely identify the subject as well as the area. The names of the POIs must follow the naming convention "[Subject-ID]_[Region]" or "[Region]_[Subject-ID]"; you may choose one of these naming conventions but it must be applied consistently across subjects. While the "Region" name may contain underscore ("_") symbols, the subject identifier may not contain this symbol because it is used to split the subject identifier from the region name.
The snapshot above shows the Patch-Of-Interest Analysis dialog filled with 10 POIs. The naming convention is used with the subject identifier at the beginning of the POI name. In this example, the subject identifiers are "AC", "CG", "MF", "NKH" and "RG" and the region names are "FFA_LH" and "PPA_LH". A separate probabilistic map can be calculated for each of these two regions across the five involved subjects.
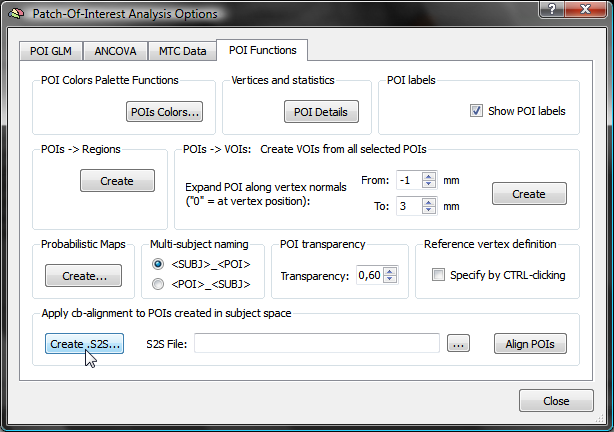
In order to apply the CBA step prior to calculation of a probabilistic map, the maps of participating subjects must be transformed using the subject's alignment (SSM) files, which are available as the result of cortex-based alignment. The alignment can be performed using the options in the Apply cb-alignment to POIs created in subject space field in the POI Analysis Options dialog.
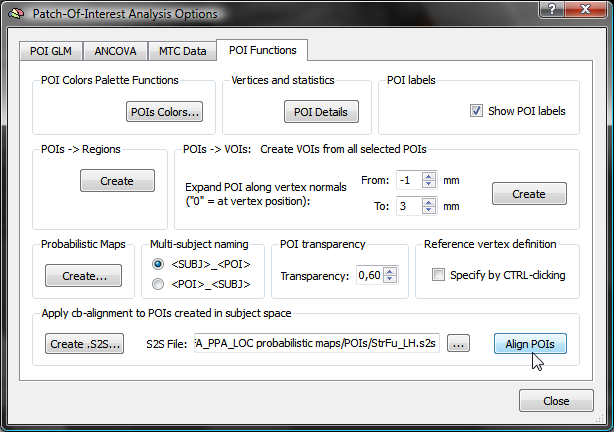
After having created or selected the proper S2S file in the S2S File entry, the POIs can be transformed from subject space into group-aligned space by clicking the Align POIs button; for more details, check the topic CBA Transformation of POIs.
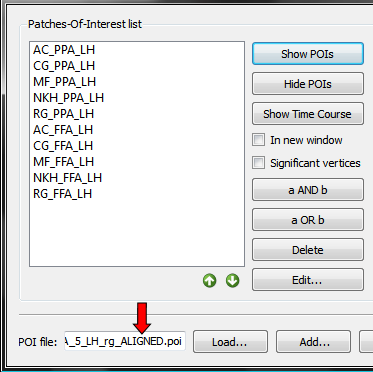
The transformed POIs are stored automatically in a file with the extension "_ALIGNED" (see snapshot above). Besides identifying the respective versions, the availability of the two files allows to create and compare probabilistic maps using the cb-unaligned and cb-aligned POIs. Such a comparison is useful to estimate the alignment gain achieved from cortex-based alignment.
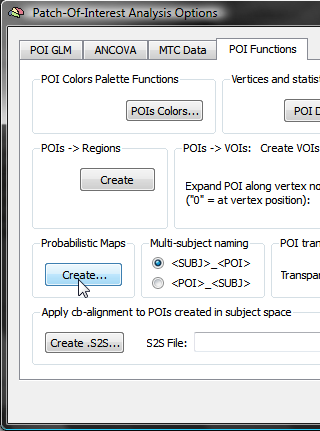
In order to specify the region(s) for which probabilistic maps should be calculated, click the Create button in the Probabilistic maps field of the POI Functions tab of the POI Analysis Options dialog (see snapshot above). This invokes the POI Probabilistic Map Creation dialog shown below.
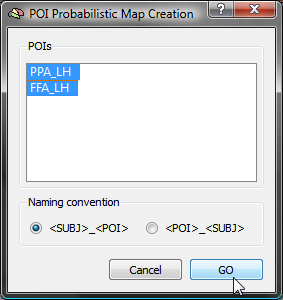
The POIs list in the dialog shows all available homologue regions without the subject identifiers (in the example the two regions "FFA_LH" and "PPA_LH"). In case that subject names are shown, the naming convention does not fit; to adjust to the chosen naming convention, click the POI_SUBJ option in the Naming convention field.
After selecting one (or more) POIs in the POIs list, click the GO button, which will calculate a separate probabilistic map for each selected POI. To select which calculated probabilistic map should be overlaid on the group cortex mesh, open the Surface Maps dialog, which will show an entry in the Maps list for each created probabilistic map. For the example data, both POIs had been selected resulting in two probabilistic maps; note that the names of the maps contain the POI region name allowing to identify the maps in case that more than one map has been calculated. In the snapshot below, the probabilistic maps for both areas ("PPA_LH" and "FFA_LH") have been selected and the overlay on the group mesh (left hemisphere) is shown on the left side.
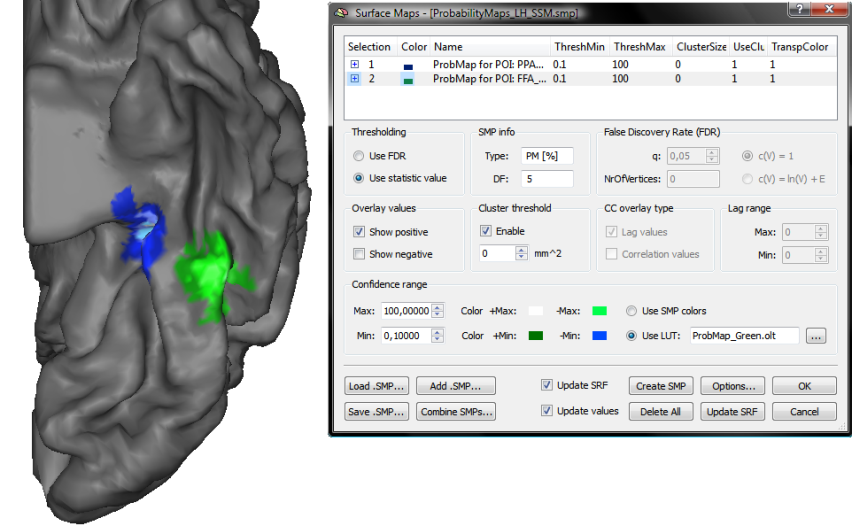
In order to improve the visualization of the probabilistic maps, an individual overlay look-up table (OLT) has been assigned for each map using the Browse LUT button in the Confidence range field of the Surface Maps dialog.
Copyright © 2014 Rainer Goebel. All rights reserved.